Admin¶
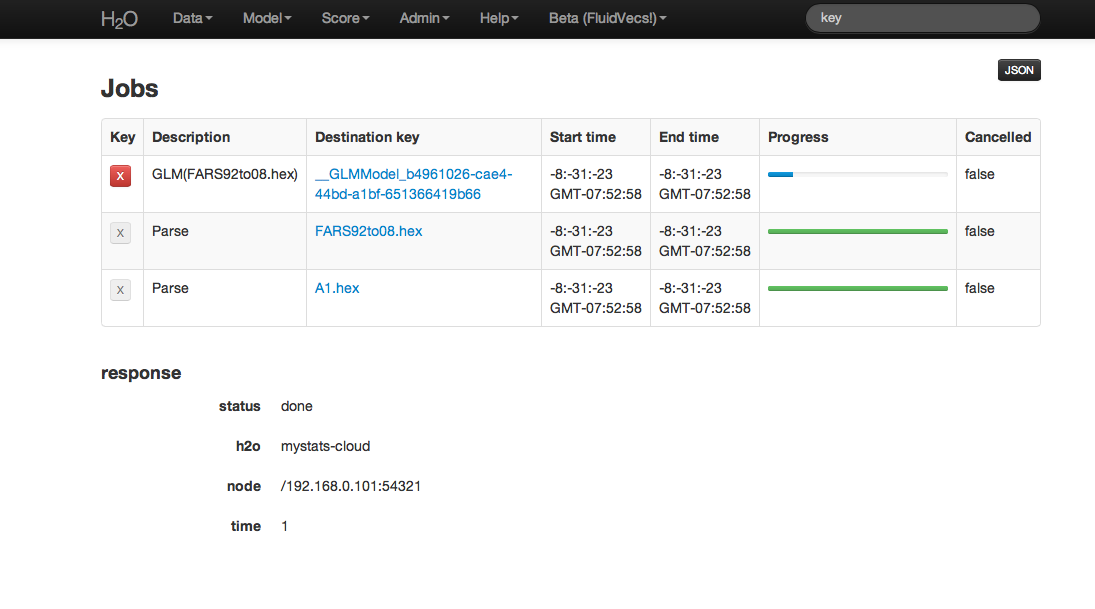
Jobs¶
Users can access information on each action undertaken in an instance of H2O by accessing Jobs under the Admin drop down menu. From here it is possible to find .hex keys associated with models and parsed data. If a an action was cancelled, that information will be displayed here as well.
Table Definitions:
Key
Table field appears with a large red “X” button for those keys that can be removed from current set of H2O objects. For instance, if a user ran several different GLM models, but wishes to keep only one of these, other models can be removed by clicking on the red X button.Description
A description of the activity associated with a particular key. For instance, a data set that has been parsed into .hex format will have “Parse” in the description field.Destination key
The actual key associated with an H2O object. This can be thought of like a corollary to a file path on a users local computer.Start Time
Time when a job was started.End Time
Time when a job completed.Progress
A status bar providing a visual indicator of job status and progress. Green and filling means that job is proceeding, but hasn’t completed, green and full means that job completed successfully, and red means that the job was unable to complete or cancelled by user.
Cluster Status¶
The status and location of a cluster can be verified by selecting Cluster Status from the Admin drop down menu.
- Table Definitions:
- In the provided table each node in an H2O cloud has a row of information.
Name
The name of the node. For example, if a user establishes three nodes on different servers, then Name will display the IP address and port in use for talking to each of those unique nodes.Num Keys
The number of keys in the distributed value store.Value size bytes
The aggregate size in bytes of all data on that node (including the set or subset of a users parsed data, but also the size in bytes of the information stored in the keys generated from modeling or data manipulation.)Free men bytes
The amount of free memory in the H2O node.Tot mem bytes
The total amount of memory in the H2O node. This value may vary over time depending on use.Max men bytes
The maximum amount of memory that the H2O node will attempt to use.Free disk bytes
The amount of free memory in the ice root. When memory needs exceed the capacity of the node, the overflow is handled by ice root, the H2O corollary to disk memory.Max disk bytes
The maximum amount of memory that can be used from ice root.Num cpus
The number of cores being used by the nodeLast contact
The last time a specific node relayed communication about its status. Last contact should read “now” or some number less than 30 seconds. If last contact is indicated to be more than 30 seconds ago, the node may be experiencing a failure.
Definitions for Fj threads hi, Fj threads low, Fj queue hi, Fj queue low, RCPS, and TCPS Active have been omitted. These fields are primarily designed for by H2O programmers, and are in development. It is likely that they will be removed in a future revision.
Log View¶
Log view provides users with a full log of activities on all nodes.
Full logs from any H2O work session can be automatically downloaded by clicking the “Download all logs” button in the upper left hand corner. When requesting help or reporting an error, please download logs, and contact us at support@0xdata.com with the logs attached.

Shutdown¶
When users are finished running a particular instance of H2O, the program should be exited by selecting Shutdown from the Admin drop down menu. Even if the user closes the browser window in which the H2O instance is running, without explicitly stopping H2O, the cluster associated with an H2O instance still exists. The user could return to the browser based interface at any time, and access all of the prior jobs within that instance of H2O. Resources are still being allocated to H2O. In order to entirely quit an instance of H2O and free up the resources allocated to the program, the user may use Shutdown to kill the cluster.
Advanced¶
Timeline: displays for the user a time ordered list of H2O status events (for example, when a cluster was started). When running a multi cluster analysis, it may happen from time to time that a node dies. This could occur for instance, if a server goes down.

Stack Dump: Advanced users and those oriented toward programming can find error information here.