Using H2O on Hadoop¶
Currently supported versions:
- CDH 5.2
- CDH 5.3
- CDH 5.4
- CDH 5.5
- CDH 5.6
- CDH 5.7
- CDH 5.8
- HDP 2.1
- HDP 2.2
- HDP 2.3
- HDP 2.4
- HDP 2.5
- HDP 2.6
- MapR 4.0
- MapR 5.0
- MapR 5.1
Important Points to Remember:
- The command used to launch H2O differs from previous versions. (Refer to the Walkthrough section.)
- Launching H2O on Hadoop requires at least 6 GB of memory
- Each H2O node runs as a mapper
- Run only one mapper per host
- There are no combiners or reducers
- Each H2O cluster must have a unique job name
-mapperXmx,-nodes, and-outputare required- Root permissions are not required - just unzip the H2O .zip file on any single node
Prerequisite: Open Communication Paths¶
H2O communicates using two communication paths. Verify these are open and available for use by H2O.
Path 1: mapper to driver
Optionally specify this port using the -driverport option in the
hadoop jar command (see “Hadoop Launch Parameters” below). This port
is opened on the driver host (the host where you entered the
hadoop jar command). By default, this port is chosen randomly by the
operating system. If you don’t want to specify an exact port but you
still wish to restrict the port to a certain range of ports, you can use
the option -driverportrange.
Path 2: mapper to mapper
Optionally specify this port using the -baseport option in the
hadoop jar command (refer to Hadoop Launch
Parameters below. This port and the next subsequent
port are opened on the mapper hosts (the Hadoop worker nodes) where the
H2O mapper nodes are placed by the Resource Manager. By default, ports
54321 (TCP) and 54322 (TCP & UDP) are used.
The mapper port is adaptive: if 54321 and 54322 are not available, H2O will try 54323 and 54324 and so on. The mapper port is designed to be adaptive because sometimes if the YARN cluster is low on resources, YARN will place two H2O mappers for the same H2O cluster request on the same physical host. For this reason, we recommend opening a range of more than two ports (20 ports should be sufficient).
Walkthrough¶
The following steps show you how to download or build H2O with Hadoop and the parameters involved in launching H2O from the command line.
Download the latest H2O release for your version of Hadoop. Refer to the H2O on Hadoop tab of the download page for either the latest stable release or the nightly bleeding edge release.
Prepare the job input on the Hadoop Node by unzipping the build file and changing to the directory with the Hadoop and H2O’s driver jar files.
unzip h2o-{{project_version}}-*.zip cd h2o-{{project_version}}-*
To launch H2O nodes and form a cluster on the Hadoop cluster, run:
hadoop jar h2odriver.jar -nodes 1 -mapperXmx 6g -output hdfsOutputDirName
The above command launches a 6g node of H2O. We recommend you launch the cluster with at least four times the memory of your data file size.
- mapperXmx is the mapper size or the amount of memory allocated to each node. Specify at least 6 GB.
- nodes is the number of nodes requested to form the cluster.
- output is the name of the directory created each time a H2O cloud is created so it is necessary for the name to be unique each time it is launched.
To monitor your job, direct your web browser to your standard job tracker Web UI. To access H2O’s Web UI, direct your web browser to one of the launched instances. If you are unsure where your JVM is launched, review the output from your command after the nodes has clouded up and formed a cluster. Any of the nodes’ IP addresses will work as there is no master node.
Determining driver host interface for mapper->driver callback... [Possible callback IP address: 172.16.2.181] [Possible callback IP address: 127.0.0.1] ... Waiting for H2O cluster to come up... H2O node 172.16.2.184:54321 requested flatfile Sending flatfiles to nodes... [Sending flatfile to node 172.16.2.184:54321] H2O node 172.16.2.184:54321 reports H2O cluster size 1 H2O cluster (1 nodes) is up Blocking until the H2O cluster shuts down...
Hadoop Launch Parameters¶
-h | -help: Display help-jobname <JobName>: Specify a job name for the Jobtracker to use; the default isH2O_nnnnn(where n is chosen randomly)-principal <kerberos principal> -keytab <keytab path> | -run_as_user <hadoop username>: Optionally specify a Kerberos principal and keytab or specify therun_as_userparameter to start clusters on behalf of the user/principal. Note that usingrun_as_userimplies that the Hadoop cluster does not have Kerberos.-driverif <IP address of mapper -> driver callback interface>: Specify the IP address for callback messages from the mapper to the driver.-driverport <port of mapper -> callback interface>: Specify the port number for callback messages from the mapper to the driver.-driverportrange <range portX-portY of mapper-> callback interface>: Specify the allowed port range of the driver callback interface, eg. 50000-55000.-network <IPv4Network1>[,<IPv4Network2>]: Specify the IPv4 network(s) to bind to the H2O nodes; multiple networks can be specified to force H2O to use the specified host in the Hadoop cluster.10.1.2.0/24allows 256 possibilities.-timeout <seconds>: Specify the timeout duration (in seconds) to wait for the cluster to form before failing. Note: The default value is 120 seconds; if your cluster is very busy, this may not provide enough time for the nodes to launch. If H2O does not launch, try increasing this value (for example,-timeout 600).-disown: Exit the driver after the cluster forms.Note: For Qubole users who include the
-disownflag, if your cluster is dying right after launch, add-Dmapred.jobclient.killjob.onexit=falseas a launch parameter.-notify <notification file name>: Specify a file to write when the cluster is up. The file contains the IP and port of the embedded web server for one of the nodes in the cluster. All mappers must start before the H2O cloud is considered “up”.-mapperXmx <per mapper Java Xmx heap size>: Specify the amount of memory to allocate to H2O (at least 6g).-extramempercent <0-20>: Specify the extra memory for internal JVM use outside of the Java heap. This is a percentage ofmapperXmx.-n | -nodes <number of H2O nodes>: Specify the number of nodes.-nthreads <maximum number of CPUs>: Specify the number of CPUs to use. Enter-1to use all CPUs on the host, or enter a positive integer.-baseport <initialization port for H2O nodes>: Specify the initialization port for the H2O nodes. The default is54321.-ea: Enable assertions to verify boolean expressions for error detection.-verbose:gc: Include heap and garbage collection information in the logs.-XX:+PrintGCDetails: Include a short message after each garbage collection.-license <license file name>: Specify the directory of local filesytem location and the license file name.-o | -output <HDFS output directory>: Specify the HDFS directory for the output.-flow_dir <Saved Flows directory>: Specify the directory for saved flows. By default, H2O will try to find the HDFS home directory to use as the directory for flows. If the HDFS home directory is not found, flows cannot be saved unless a directory is specified using-flow_dir.
Accessing S3 Data from Hadoop¶
H2O launched on Hadoop can access S3 Data in addition to to HDFS. To enable access, follow the instructions below.
Edit Hadoop’s core-site.xml, then set the HADOOP_CONF_DIR
environment property to the directory containing the core-site.xml
file. For an example core-site.xml file, refer to Core-site.xml Example. Typically, the configuration directory for
most Hadoop distributions is /etc/hadoop/conf.
You can also pass the S3 credentials when launching H2O with the Hadoop
jar command. Use the -D flag to pass the credentials:
hadoop jar h2odriver.jar -Dfs.s3.awsAccessKeyId="${AWS_ACCESS_KEY}" -Dfs.s3n.awsSecretAccessKey="${AWS_SECRET_KEY}" -n 3 -mapperXmx 10g -output outputDirectory
where AWS_ACCESS_KEY represents your user name and
AWS_SECRET_KEY represents your password.
Then import the data with the S3 URL path:
To import the data from the Flow API:
importFiles [ "s3n:/path/to/bucket/file/file.tab.gz" ]
To import the data from the R API:
h2o.importFile(path = "s3n://bucket/path/to/file.csv")
To import the data from the Python API:
h2o.import_frame(path = "s3n://bucket/path/to/file.csv")
YARN Best Practices¶
YARN (Yet Another Resource Manager) is a resource management framework. H2O can be launched as an application on YARN. If you want to run H2O on Hadoop, essentially, you are running H2O on YARN. If you are not currently using YARN to manage your cluster resources, we strongly recommend it.
Using H2O with YARN¶
When you launch H2O on Hadoop using the hadoop jar command, YARN
allocates the necessary resources to launch the requested number of
nodes. H2O launches as a MapReduce (V2) task, where each mapper is an
H2O node of the specified size.
hadoop jar h2odriver.jar -nodes 1 -mapperXmx 6g -output hdfsOutputDirName
Occasionally, YARN may reject a job request. This usually occurs because either there is not enough memory to launch the job or because of an incorrect configuration.
If YARN rejects the job request, try launching the job with less memory
to see if that is the cause of the failure. Specify smaller values for
-mapperXmx (we recommend a minimum of 2g) and -nodes (start
with 1) to confirm that H2O can launch successfully.
To resolve configuration issues, adjust the maximum memory that YARN will allow when launching each mapper. If the cluster manager settings are configured for the default maximum memory size but the memory required for the request exceeds that amount, YARN will not launch and H2O will time out. If you are using the default configuration, change the configuration settings in your cluster manager to specify memory allocation when launching mapper tasks. To calculate the amount of memory required for a successful launch, use the following formula:
YARN container size (mapreduce.map.memory.mb) =-mapperXmxvalue + (-mapperXmx*-extramempercent[default is 10%])
The mapreduce.map.memory.mb value must be less than the YARN memory
configuration values for the launch to succeed.
Configuring YARN¶
For Cloudera, configure the settings in Cloudera Manager. Depending on how the cluster is configured, you may need to change the settings for more than one role group.
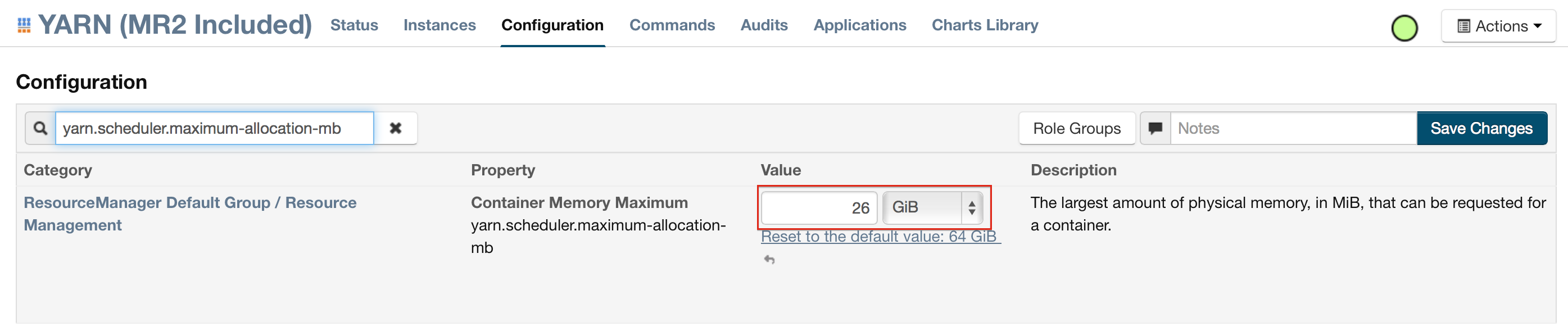
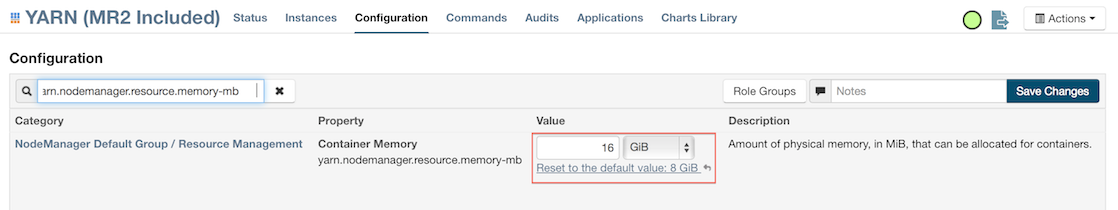
Click Configuration and enter the following search term in quotes: yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb.
Enter the amount of memory (in GB) to allocate in the Value field. If more than one group is listed, change the values for all listed groups.
Click the Save Changes button in the upper-right corner.
Enter the following search term in quotes: yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb
Change the value, click the Save Changes button in the upper-right corner, and redeploy.
For Hortonworks, configure the settings in Ambari.
- Select YARN, then click the Configs tab.
- Select the group.
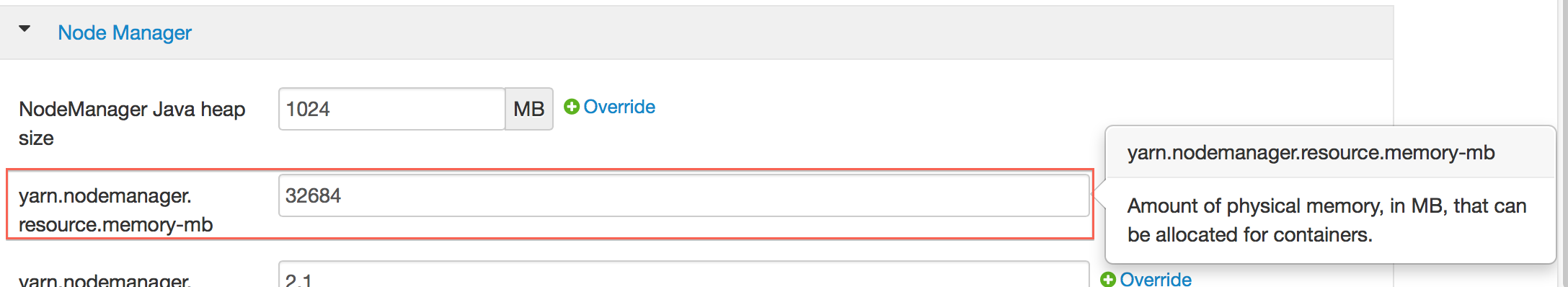
- In the Node Manager section, enter the amount of memory (in MB) to allocate in the yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb entry field.
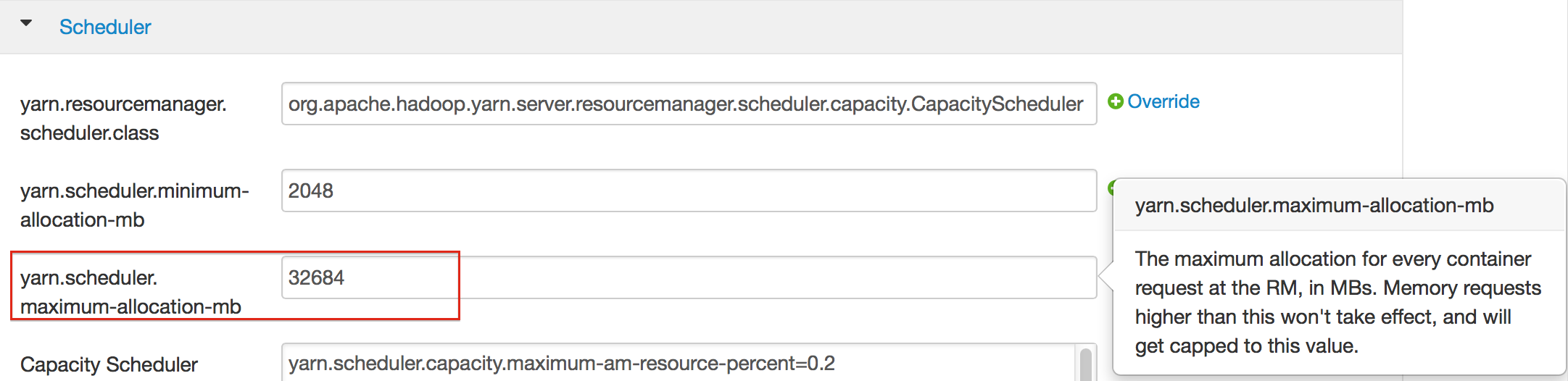
- In the Scheduler section, enter the amount of memory (in MB) to allocate in the yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb entry field.
- Click the Save button at the bottom of the page and redeploy the cluster.
For MapR:
- Edit the yarn-site.xml file for the node running the ResourceManager.
- Change the values for the
yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mbandyarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mbproperties. - Restart the ResourceManager and redeploy the cluster.
To verify the values were changed, check the values for the following properties:
- <name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb</name>
- <name>yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb</name>
Limiting CPU Usage¶
To limit the number of CPUs used by H2O, use the -nthreads option
and specify the maximum number of CPUs for a single container to use.
The following example limits the number of CPUs to four:
hadoop jar h2odriver.jar -nthreads 4 -nodes 1 -mapperXmx 6g -output hdfsOutputDirName
Note: The default is 4*the number of CPUs. You must specify at
least four CPUs; otherwise, the following error message displays:
ERROR: nthreads invalid (must be >= 4)
Specifying Queues¶
If you do not specify a queue when launching H2O, H2O jobs are submitted to the default queue. Jobs submitted to the default queue have a lower priority than jobs submitted to a specific queue.
To specify a queue with Hadoop, enter -Dmapreduce.job.queuename=<my-h2o-queue> (where <my-h2o-queue> is the name of the queue) when launching
Hadoop.
For example,
hadoop jar h2odriver.jar -Dmapreduce.job.queuename=<my-h2o-queue> -nodes <num-nodes> -mapperXmx 6g -output hdfsOutputDirName
Specifying Output Directories¶
To prevent overwriting multiple users’ files, each job must have a
unique output directory name. Change the -output hdfsOutputDir
argument (where hdfsOutputDir is the name of the directory.
Alternatively, you can delete the directory (manually or by using a script) instead of creating a unique directory each time you launch H2O.
Customizing YARN¶
Most of the configurable YARN variables are stored in yarn-site.xml.
To prevent settings from being overridden, you can mark a config as
“final.” If you change any values in yarn-site.xml, you must restart
YARN to confirm the changes.
Accessing Logs¶
Access logs for a YARN job with the yarn logs -applicationId <application_id>
command from a terminal. Note that this command must be run by
the same userid as the job owner, and only after the job has finished.