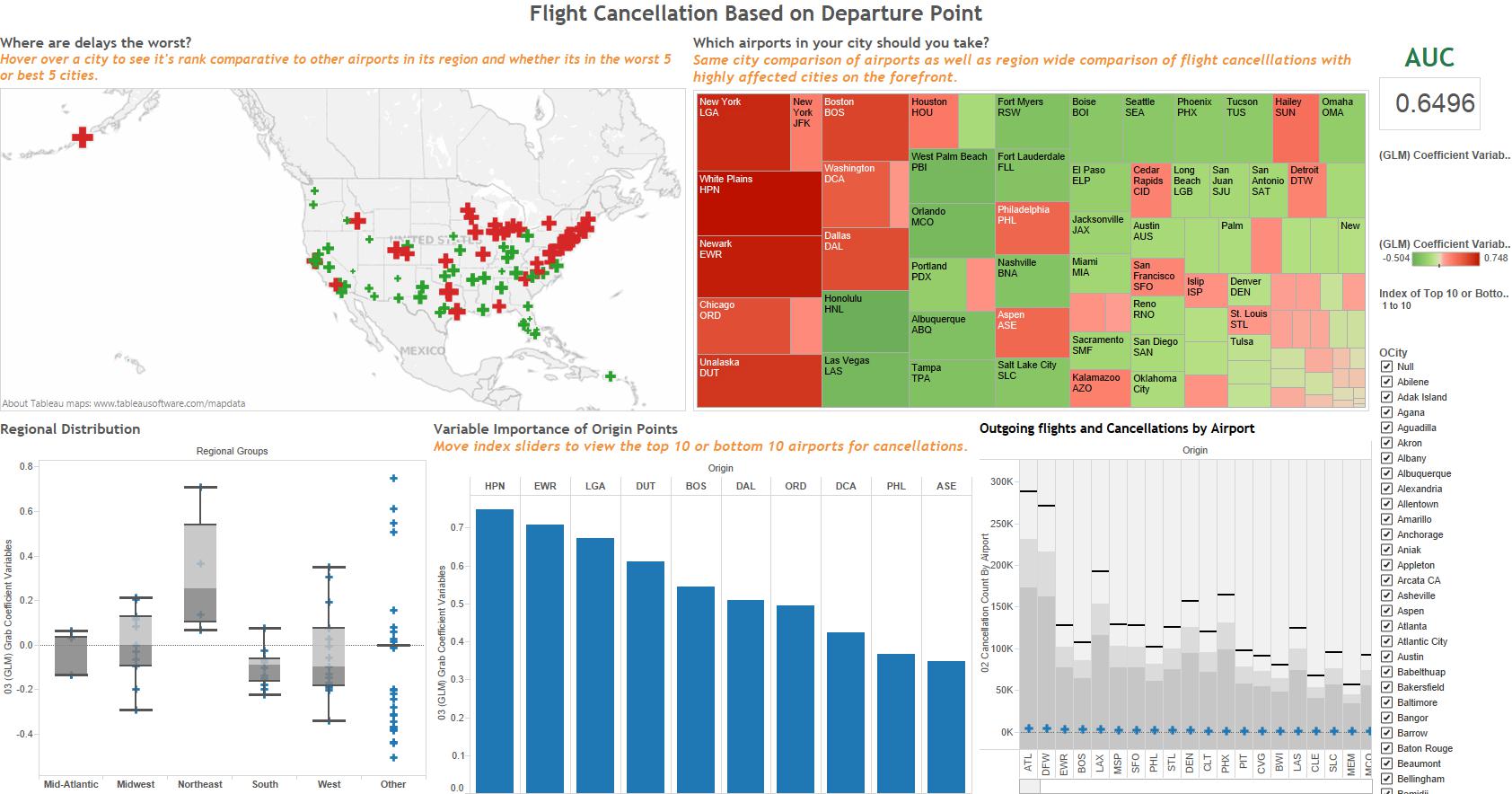
Tableau 8.1¶
Have H2O Installed¶
Pre-requisites :
- 64-bit Oracle Java 1.6+
- Tableau 8.1 installed
- H2O installed in R (follow the download guide Install H2O package in R)
Metadata¶
Tableau requires some sort of data input to run, but when dealing with immensely big data as a H2O user would typically do, it is impractical and unnecessarily time-consuming to feed all the data into Tableau. So the solution is to create a small metadata file that can be easily loaded from the disk.
Note: In particular, geographic attributes like cities and latitude/longitude coordinates need to be imported into Tableau. Aggregates and calculated fields cannot be converted, so even if you have a vector of cities (New York City, San Francisco, Houston, Austin, Seattle) as a output from R into Tableau as a new measure, you cannot convert the measure into geographical points.
The metadata is a file with factor levels of the data frame that give a quick overview of the unique input values and cardinality of each column. This format will also allow the user to calculate across the table, making it easier to actually visualize some of the data coming from H2O. For example, if a column has a 352 categorical values and a binomial GLM is run with 352 coefficients in the output, Tableau allows plotting of the coefficients against the column.
The following data is a truncated metadata file for 116 million rows airline data set. This particular metadata file is only about 352 rows. A extra column was prepended to the data file to grab the column names of the actual data set. This column helps populate certain parameters in the workbook.
Colnames Year Month DayofMonth DayOfWeek UniqueCarrier Origin OCity
Year 1988 1 1 1 PI SYR Syracuse
Month 1989 2 2 2 PS LGA New York
DayofMonth 1990 3 3 3 TW JFK New York
DayOfWeek 1991 4 4 4 UA UCA Utica
DepTime 1992 5 5 5 WN CHO Charlottesville
CRSDepTime 1993 6 6 6 EA CLT Charlotte
ArrTime 1994 7 7 7 HP EWR Newark
CRSArrTime 1996 8 8 NW LYH Lynchburg
UniqueCarrier 1998 9 9 CO ROA Roanoke
FlightNum 2000 10 10 DL BWI Baltimore
TailNum 2001 11 11 AA MYR Myrtle Beach
ActualElapsedTime 2003 12 12 US GSO Greensboro
CRSElapsedTime 2004 13 AS ISP Islip
AirTime 2005 14 AQ CHS Charleston
ArrDelay 2006 15 MQ ORF Norfolk
DepDelay 2007 16 OO BGM Binghamton
Origin 2008 17 XE LAX Los Angeles
Dest 18 EV SEA Seattle
Distance 19 DH SJC San Jose
Create R, Tableau, and Data Connections¶
Step 1
Install Rserve (the package built to create Rserve), load the Rserve library, and run Rserve or run Rserve with your desired port.
> install.packages("Rserve")
> library(Rserve)
> run.Rserve(port=6311)
Step 2
Open Demo_Template_8.1.twb, which should have all the calculated fields containing R scripts already in the sidebar. Navigate to “Help > Settings and Performance > Manage R Connection” to establish a connection to the Rserve.
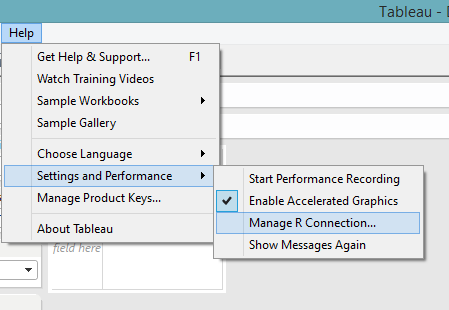
Input the server ip address and port:
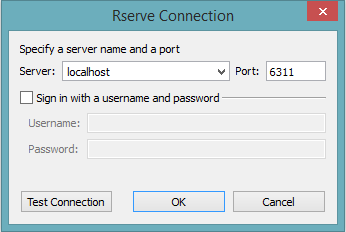
Step 3
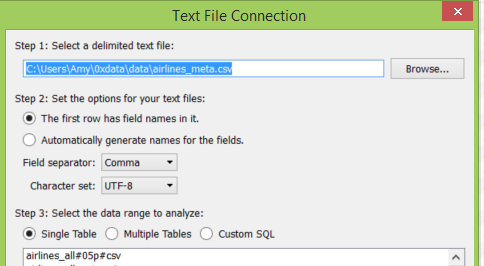
Set the workbook’s connection to the airlines_meta.csv data by navigating to the data section on the left sidebar, right-clicking on the airlines_meta, and choosing “Edit Connection.”
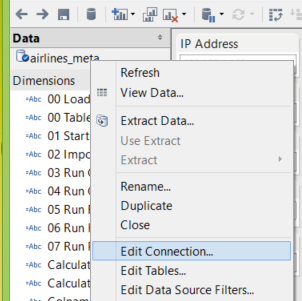
Provide the location of the airlines_meta.csv file and submit the new path.
Step 4
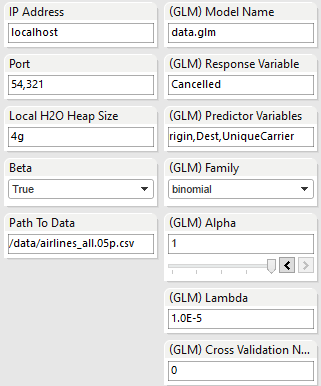
Configure the IP Address and Port that H2O uses to launch, as well as the path to the full airlines data file. Fill in the parameters to create a new GLM model. For documentation about the parameters, refer to our GLM documentation page Generalized Linear Model.
Execute Scripts¶
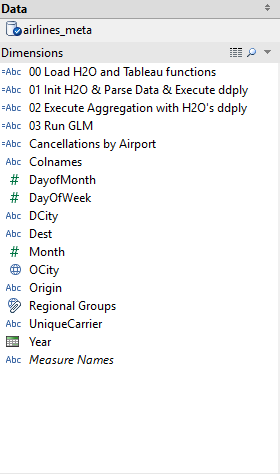
Double-click the calculated fields under “Dimensions” in the order in which they are listed:
- Execute “00 Load H2O and Tableau functions” to run library(h2o) and define other R functions to be used in Tableau.
- Execute “01 Init H2O & Parse Data” will run h2o.init() and h2o.importFile().
- Execute “02 Compute Aggregation with H2O’s ddply” will run h2o.ddply() and create measures for use in “Flights By Month” and “Flights By Airport” worksheets.
- Execute “03 Run GLM” to build a GLM model in H2O and grab back coefficient values that will be plotted in multiple worksheets.