PCA Tutorial¶
This tutorial describes how to perform a PCA analysis in H2O.
If you have never used H2O before, refer to the quick start guide for additional instructions on how to run H2O: Getting Started From a Downloaded Zip File.
When to Use PCA¶
Use PCA to reduce dimensions and solve issues of multicollinearity in high dimension data.
Getting Started¶
This tutorial uses a publicly available data set that can be found at: http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Arrhythmia
The original data are the Arrhythmia data set made available by UCI Machine Learning Repository. They are composed of 452 observations and 279 attributes.
Before modeling, parse data into H2O:
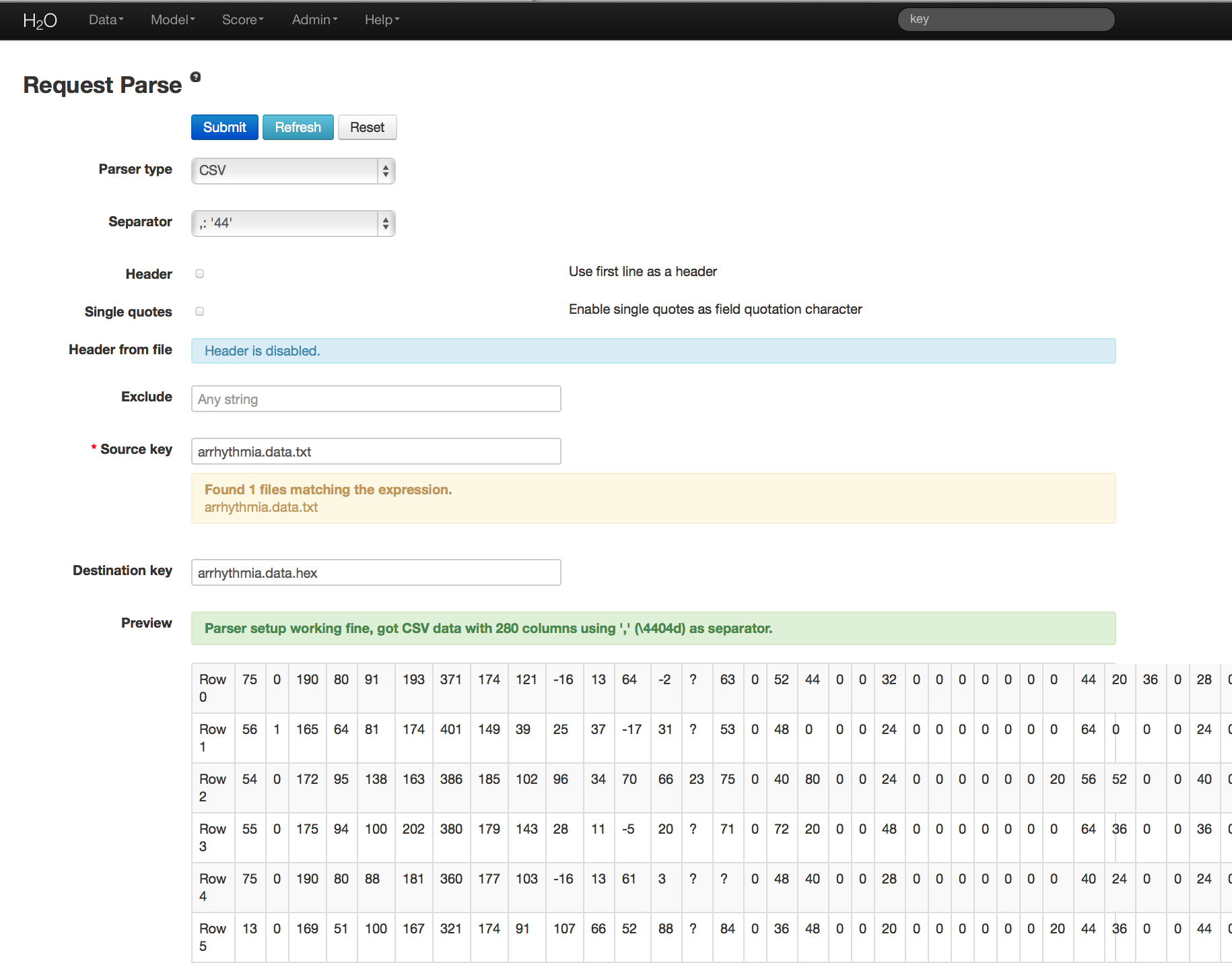
- From the drop-down Data menu, select Upload and use the uploader to upload data.
- On the “Request Parse” page that appears, check the “header” checkbox if the first row of the data set is a header. No other changes are required.
- Click Submit. Parsing data into H2O generates a .hex key of the form “data name.hex”
Building a Model¶
Once data are parsed, a horizontal menu displays at the top of the screen reading “Build model using ... ”. Select PCA here, or go to the drop-down Model menu and select PCA.
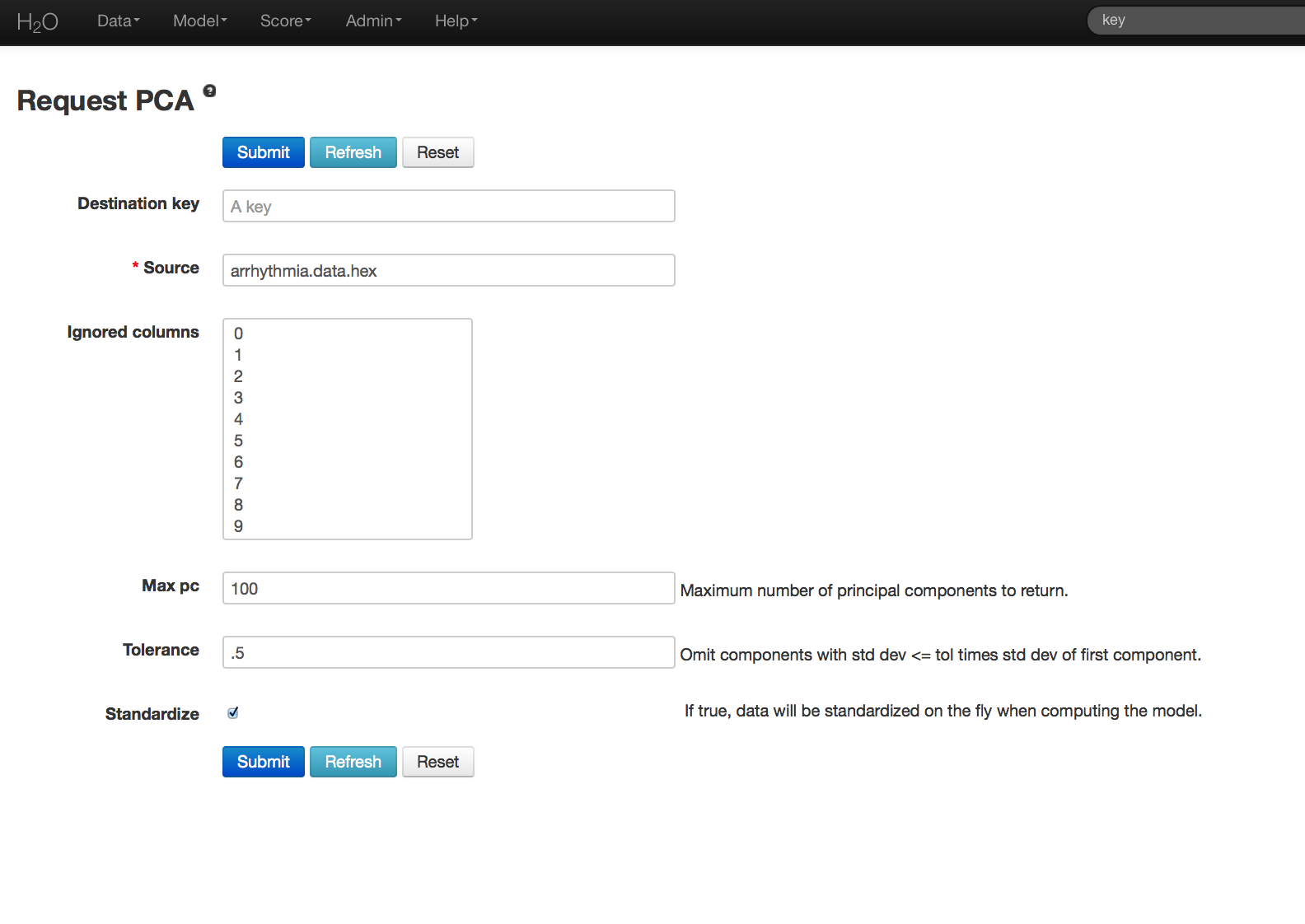
In the “source” field, enter the .hex key for the Arrhythmia data set.
In the “Ignored Columns” field, select the set of columns to omit from the analysis.
Note: PCA ignores categorical variables and constant columns. Categoricals can be included by expanding the categorical into a set of binomial indicators.
To specify the maximum number of principal components to be returned, enter a value in the “max pc” field. In this example, the maximum number of components is 100.
To omit components exhibiting low standard deviation (which indicates a lack of contribution to the overall variance observed in the data), enter a value in the “tolerance” field. In this example, set Tolerance to .5.
To standardize, check the “standardize” checkbox. Standardizing is highly recommended; if you do not use standardization, the results can include components that are dominated by variables that appear to have larger variances relative to other attributes purely as a matter of scale, rather than true contribution.
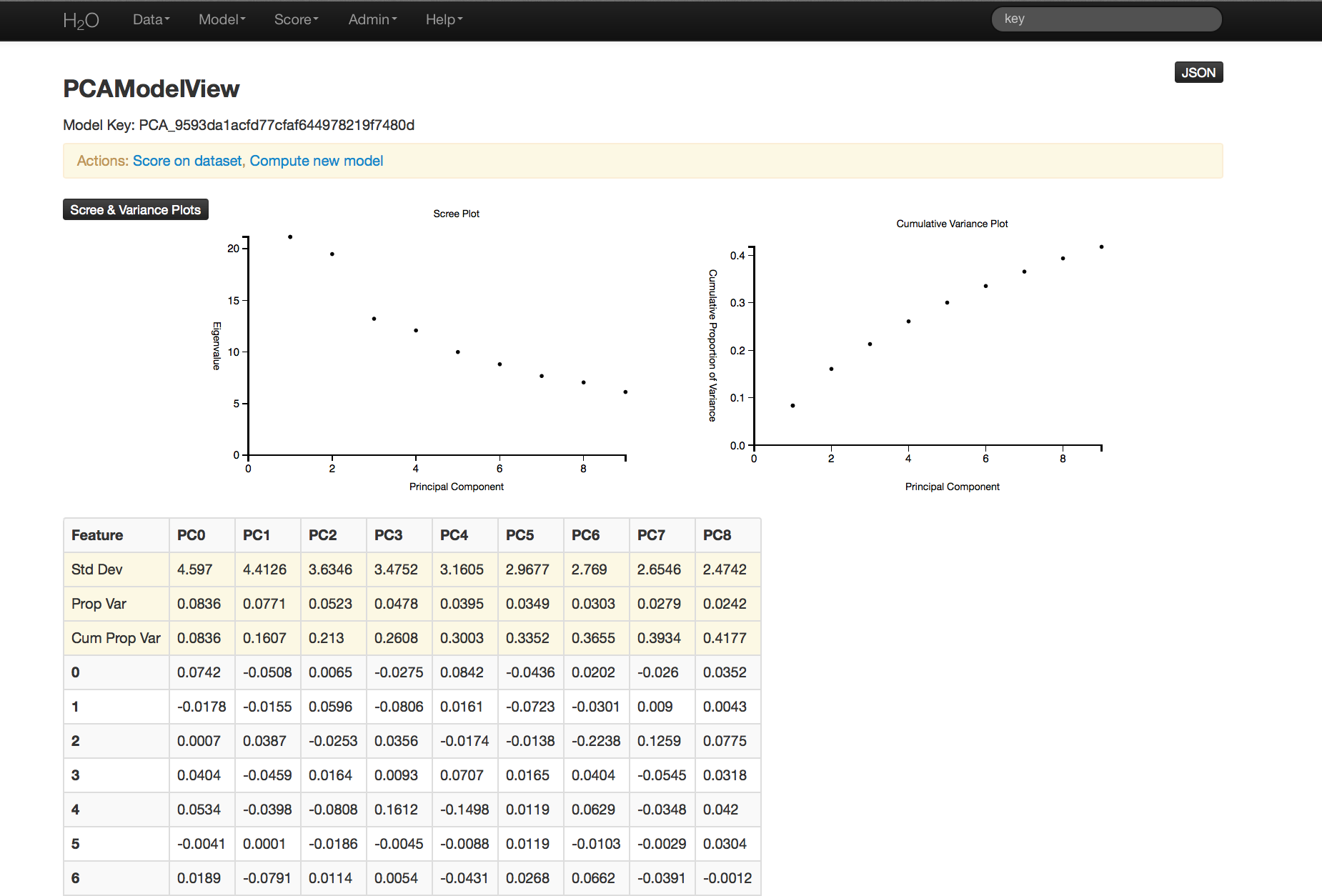
PCA Results¶
The PCA output displays a table with the number of components indicated by the most restrictive criteria for this particular case. In this example, a maximum of 100 components are requested and tolerance is .5.
The output also include scree and cumulative variance plots for the components. To view this information, click the black button labeled “Scree and Variance Plots” at the top left of the results page. A scree plot shows the variance of each component, while the cumulative variance plot shows the total variance accounted for by the set of components.
Note: To replicate results between H2O and R, we recommend disabling standardization and cross validation in H2O, or specifying the values in R.