Troubleshooting H2O¶
Download and Send Us Your Logs¶
Step 1
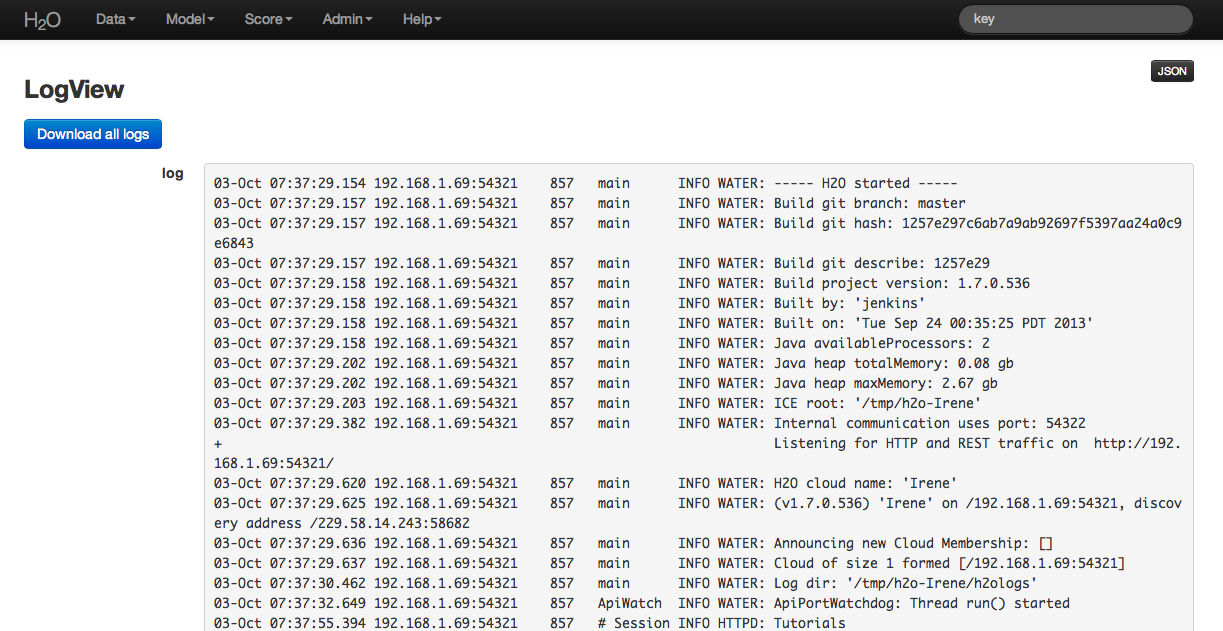
Through the drop down menu Admin go to Log View.
On the Log View page there is a Download Logs button in the upper left hand corner. Click on it to download your logs.
Step 2
From your email account contact h2ostream@googlegroups.com with a brief description of the error you encountered, and your contact information. Attach the downloaded H2O logs downloaded from log view to the email before sending.
Step 3
We will route your email to the correct engineer or data scientist and work to resolve your issue.
Hadoop - Copy and Paste Your YARN Logs¶
In the event H2O fails to launch properly on Hadoop send us the YARN logs.
When launching H2O on Hadoop the following messages will show up first regardless of failure or success, otherwise the argument has not been entered correctly:
amy@mr-0xb1:~/h2o-2.5.0.99999/hadoop$ hadoop jar h2odriver_hdp1.3.2.jar water.hadoop.h2odriver
-libjars ../h2o.jar -mapperXmx 10g -nodes 4 -output output903 -verbose:class
Determining driver host interface for mapper->driver callback...
[Possible callback IP address: 192.168.1.161]
[Possible callback IP address: 127.0.0.1]
Using mapper->driver callback IP address and port: 192.168.1.161:37244
(You can override these with -driverif and -driverport.)
Driver program compiled with MapReduce V1 (Classic)
Memory Settings:
mapred.child.java.opts: -Xms10g -Xmx10g -verbose:class
mapred.map.child.java.opts: -Xms10g -Xmx10g -verbose:class
Extra memory percent: 10
mapreduce.map.memory.mb: 11264
Job name 'H2O_74206' submitted
JobTracker job ID is 'job_201407040936_0030'
For YARN users, logs command is 'yarn logs -applicationId application_201407040936_0030'
Waiting for H2O cluster to come up...
To view the YARN log execute the command specify on line “For YARN users, logs command is <>”
yarn logs -applicationId application_201407040936_0030
Copy and email the logs to support@0xdata.com or paste to h2ostream@googlegroups.com with a brief description of your Hadoop environment including the distribution and version of Hadoop.
Other Common Troubleshooting Topics¶
Common Question: Why is “Upload” is no longer working?
This can occur when a user’s local disk is full or almost full. Free up space on your local disk, and the behavior should resolve.
Common Question: I launched H2O instances on my nodes but why won’t they cloud up?
When launching without specifying the IP address by adding argument -ip:
$ java -Xmx20g -jar h2o.jar -flatfile flatfile.txt -port 54321
and multiple local IP addresses are detected, H2O will fall back to default 127.0.0.1 as shown below:
10:26:32.266 main WARN WATER: Multiple local IPs detected:
+ /198.168.1.161 /198.168.58.102
+ Attempting to determine correct address...
10:26:32.284 main WARN WATER: Failed to determine IP, falling back to localhost.
10:26:32.325 main INFO WATER: Internal communication uses port: 54322
+ Listening for HTTP and REST traffic on http://127.0.0.1:54321/
10:26:32.378 main WARN WATER: Flatfile configuration does not include self:
/127.0.0.1:54321 but contains [/192.168.1.161:54321, /192.168.1.162:54321]
To avoid falling back to 127.0.0.1 on servers with multiple local IP addresses just run the command with the -ip argument forcing a launch at the appropriate location:
$ java -Xmx20g -jar h2o.jar -flatfile flatfile.txt -ip 192.168.1.161 -port 54321
Common Question: Why are my string entries being converted into NAs during Parse?
At the moment columns with numeric values will have the string entries converted to NAs when the data is being ingested:
Data Frame in R Data Frame in H2O
V1 V2 V3 V4 V1 V2 V3 V4
1 1 6 11 A 1 1 6 11 NA
2 2 B A A 2 2 NA NA NA
3 3 A 13 18 3 3 NA 13 18
4 4 C 14 19 4 4 NA 14 19
5 5 10 15 20 5 5 10 15 20
If the numeric values in the column were meant to be additional factor levels then you can concatenate the values with a string and the column will parse as a enumerator column:
V1 V2 V3 V4
1 1 i6 i11 A
2 2 B A A
3 3 A i13 i18
4 4 C i14 i19
5 5 i10 i15 i20
R and H2O¶
In order for H2O and R to work together, an instance of H2O must be running, and that instance of H2O must be specified in the R workspace. If the H2O instance is terminated the H2O package in R will no longer work because R will no longer be able to send information to H2O’s distributed analysis, and will no longer be able to get info mation back. Even if a new instance of H2O is started with the exact same IP and port number, users will need to reestablish the connection between H2O and R using the call h2o.init(), and will have to restart their H2O work session.
Updating the R Package aka. Avoid Version Mismatch!
H2O’s R package is now available for download on CRAN but typically the 0xdata team continues to push new releases faster than CRAN typically upload more recent packages. To avoid a version mismatch when upgrading or changing your version of H2O in R please run through the following steps :
Close any Java instances up to kill any rogue H2O instances that hasn’t been properly shut down or terminated.
Uninstall previous version of H2O from R by running :
if ("package:h2o" %in% search()) { detach("package:h2o", unload=TRUE) } if ("h2o" %in% rownames(installed.packages())) { remove.packages("h2o") }For Windows especially check to make sure there are no remanants of H2O in your personal R library.
Download and/or install the H2O package version by following the instructions in our R user documentation.
If you still run into trouble with h2o.init() try running in the terminal:
$ java -Xmx1g -jar h2o.jar
Go back to R and try running h2o.init() again. If the problem persist please contact us at support@0xdata.com.
Common Question: How Do I Manage Dependencies in R?
The H2O R package utilizes other R packages (like lattice, and curl). From time to time R will fail to download from CRAN and give an error. In that case it’s best to get the binary from C RAN directly and install the package manually using the call:
>install.packages("path/to/fpc/binary/file", repos = NULL, type = "binary")
Users may find this page on installing dependencies helpful:
http://stat.ethz.ch/R-manual/R-devel/library/utils/html/install.packages.html
Common Question: Why is only one CPU being used when I start H2O from R?
Depending on how you got your version of R, it may be configured to run with only one CPU by default. This is particularly common for Linux installations. This can affect H2O when you use the h2o.init() function to start H2O from R.
You can tell if this is happening by looking in /proc/<nnnnn>/status at the Cpus_allowed bitmask (where nnnnn is the PID of R).
(/proc/<nnnnn>/status: This configuration is BAD!)
Cpus_allowed: 00000001
Cpus_allowed_list: 0
If you see a bitmask with only one CPU allowed, then any H2O process forked by R will inherit this limitation. To work around this, set the following environment variable before starting R:
$ export OPENBLAS_MAIN_FREE=1
$ R
Now you should see something like the following in /proc/<nnnnn>/status
(/proc/<nnnnn>/status: This configuration is good.)
Cpus_allowed: ffffffff
Cpus_allowed_list: 0-31
At this point, the h2o.init() function will start an H2O that can use more than one CPU.
Internal Server Error in R
brew install gnu-tar
cd /usr/bin
sudo ln -s /usr/local/opt/gnu-tar/libexec/gnubin/tar gnutar
H2O On Windows¶
Using CMD Shell as an alternative to using terminal for windows users allows windows users to execute instructions as written for installign and running H2O in general.
In order to install and run R on Windows 8 (any and all R packages, including those distributed by H2O) users will need read and write persmissions to
Tunneling between servers with H2O¶
Step 1
Log in to the machine where H2O will run using ssh
Step 2
Start an instance of H2O by locating the working directory and calling a java command similar to the following ( the port number chosen here is arbitrary and users might choose something different).
$ java -jar h2o.jar -port 55599
This returns output similar to the following:
irene@mr-0x3:~/target$ java -jar h2o.jar -port 55599
04:48:58.053 main INFO WATER: ----- H2O started -----
04:48:58.055 main INFO WATER: Build git branch: master
04:48:58.055 main INFO WATER: Build git hash: 64fe68c59ced5875ac6bac26a784ce210ef9f7a0
04:48:58.055 main INFO WATER: Build git describe: 64fe68c
04:48:58.055 main INFO WATER: Build project version: 1.7.0.99999
04:48:58.055 main INFO WATER: Built by: 'Irene'
04:48:58.055 main INFO WATER: Built on: 'Wed Sep 4 07:30:45 PDT 2013'
04:48:58.055 main INFO WATER: Java availableProcessors: 4
04:48:58.059 main INFO WATER: Java heap totalMemory: 0.47 gb
04:48:58.059 main INFO WATER: Java heap maxMemory: 6.96 gb
04:48:58.060 main INFO WATER: ICE root: '/tmp'
04:48:58.081 main INFO WATER: Internal communication uses port: 55600
+ Listening for HTTP and REST traffic on http://192.168.1.173:55599/
04:48:58.109 main INFO WATER: H2O cloud name: 'irene'
04:48:58.109 main INFO WATER: (v1.7.0.99999) 'irene' on
/192.168.1.173:55599, discovery address /230 .252.255.19:59132
04:48:58.111 main INFO WATER: Cloud of size 1 formed [/192.168.1.173:55599]
04:48:58.247 main INFO WATER: Log dir: '/tmp/h2ologs'
Step 3
Log into the remote machine where the running instance of H2 O will be forwarded using a command similar to the following (where users specified port numbers and IP address will be different)
ssh -L 55577:localhost:55599 irene@192.168.1.173
Step 4
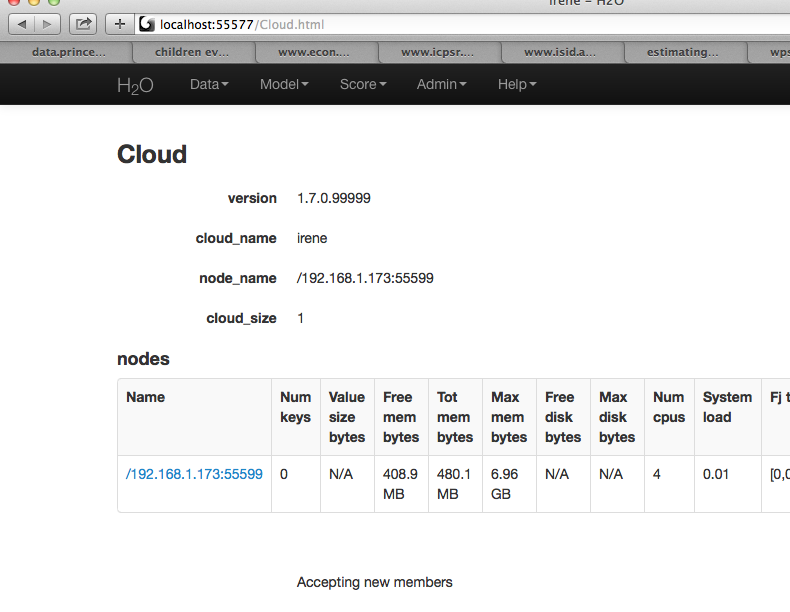
Check cluster status
You are now using H2O from localhost:55577, but the instance of H2O is running on the remote server (in this case the server with the ip address 192.168.1.xxx) at port number 55599.
To see this in action note that the web UI is pointed at localhost:55577, but that the cluster status shows the cluster running on 192.168.1.173:55599